Technology as Enabler of 2016 HR Trends: Personalized Learning and Transparency
Recently, I published an article on some of the major disruptions happening in the workplace and the role that technology has played (is playing) in
Recently, I published an article on some of the major disruptions happening in the workplace and the role that technology has played (is playing) in

Are new technologies emerging so rapidly that organizations can’t keep pace? What’s ahead in HR innovation and how should we prepare?

What does a future-ready workforce look like? Business collaboration and learning expert Dan Pontefract says it features a special kind of leader
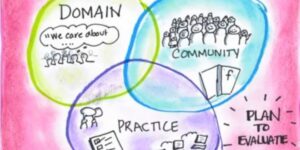
Digital communities: Why are they a challenge for businesses to create and maintain? How can enterprise organizations up their community game?
How can your organization make collaboration a competitive advantage? Here are some great ideas to put your workforce on the right track…